 COVID-19
COVID-19
The COVID-19 pandemic mounted an unprecedented global effort to curb the impacts of its spread. Because of the impacts the pandemic has had on our society and culture, the underlying biological mechanisms of the novel coronavirus that causes COVID-19 (SARS-CoV-2) are currently under extensive study and can be applied to our existing understanding of the mechanisms and evolution of infectious diseases. A complete understanding of the pandemic involves looking at the evolutionary origins and molecular features of the virus, trends in transmission, behavioral and cultural responses, and the rapid development of novel vaccine technologies. This case examines the evolution, the biological mechanisms, and the societal impacts of the SARS-CoV-2 virus and the disease it causes, COVID-19.
Viral and Cell Biology
What is a virus?
A virus is a non-living, submicroscopic pathogen that infects living host cells in order to replicate. All types of living organisms can be infected by viruses, including plants, animals, fungi, bacteria, and archaea. Viruses attack living cells and insert genetic material (either DNA or RNA) into the cell. The living cells then create proteins based on the information in the genetic material. Those proteins produce more copies of the virus. Viruses have evolved to use the energy and existing mechanisms in host cells to reproduce at the expense of the host. There is a wide diversity of viruses. Generally, viruses are placed into one of seven classes according to how their genome is stored and transferred into the host cell. Most viruses that infect humans are positive-sense single-stranded RNA viruses, including coronaviruses such as SARS-CoV-2. The current leading hypothesis is viruses independently evolved more than once, whereas all living organisms are thought to have evolved from the same ancestor. This complicates any attempt to create a phylogeny including all viruses because not all viruses share a common ancestor. However, it is relatively easy to determine evolutionary relationships between viruses with very similar genomes. A detailed phylogeny of the SARS-CoV-2 is continuously being updated as the virus mutates and evolved.
Viral epidemiology
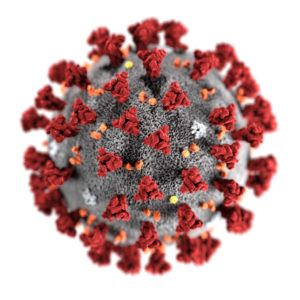
The anatomy of SARS-CoV-2
Like other coronaviruses, SARS-CoV-2
The life cycle of SARS-CoV-2
Viral Genetics
The SARS-CoV-2 genome
The spike (S) gene
SARS-CoV-2 mutation rate
Viral Origins & Phylogenetics
Zoonotic spillover
SARS-CoV-2 phylogeny
Omicron: Hidden evolution
Variant Evolution
The evolution of delta
The evolution of omicron
